Navigating the Information Landscape: Understanding Misinformation and Disinformation
In our increasingly digital world, information is more accessible than ever before. However, this wealth of information also comes with a significant challenge – distinguishing between reliable and misleading content. Misinformation and disinformation are two terms that have gained prominence in recent years, and understanding them is crucial for individuals in today’s information age. Moreover, various forms of literacy, such as digital literacy, news literacy, media literacy, disciplinary literacy, and information literacy, play essential roles in helping individuals navigate this complex landscape.
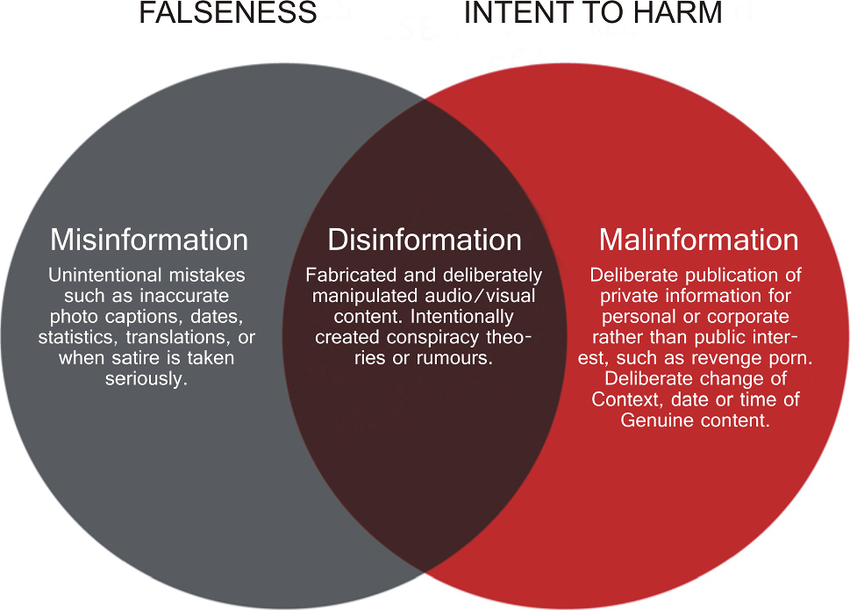
Misinformation and Disinformation
Before diving into the different types of literacy, it is essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of misinformation and disinformation.
Misinformation refers to the dissemination of false or misleading information, but it is typically not spread with the intent to deceive. Instead, it may result from errors, misunderstandings, or misinterpretations of facts. Misinformation can be unintentional, and those sharing it are often unaware that the information is inaccurate.
On the other hand, disinformation involves the deliberate act of sharing false or misleading information with the intent to deceive, manipulate, or harm others. It is a malicious form of misinformation, often driven by ulterior motives, such as spreading propaganda, gaining a competitive advantage, or sowing confusion and discord.
Fact-Checking Tools
Map Checking
URL: www.mapchecking.com
Purpose:
● Estimate crowd size for any given geographical location
● Ability to check potential crowd size from just a section of street to large scale area
● Givesrange of crowd size numbers
Reverse Image Search
- Google Lens
- TinEye Reverse Image Search (https://tineye.com/)
- Bing Visual Search
- Yandex
InVid & WeVerify
URL: (both links will take you to the plugin)
● https://weverify.eu/verification-plugin/
● https://www.invid-project.eu/tools-and-services/invid-verification-plugin/
Purpose:
● Identifies cheapfakes
● Pulls frames from videos then you can click the frame to search
Read More https://www.lankaxpress.com/fact-checking-tools-to-help-stop-fake-news/
What is Fake news?
Fake news refers to false or misleading information presented as if it were true news. It often involves the deliberate spreading of fabricated or deceptive stories, typically through traditional news outlets, social media, or other online platforms.
What is fact-checking?
Fact-checking is the process of independently verifying the accuracy and truthfulness of information, claims, statements, or assertions made in news articles, speeches, social media posts, or other forms of communication. The goal of fact-checking is to provide the public with reliable and verified information, which helps in distinguishing between true and false or misleading claims.
Types of Literacies
Digital Literacy
Digital literacy is the ability to comprehend and analyze the workings of computational technology. It encompasses understanding the basics of using computers, the internet, and software applications. In an era where digital tools and platforms are ubiquitous, digital literacy is crucial for both navigating technology and evaluating online information.
News Literacy
News literacy is the capacity to critically assess and judge the credibility of news information. In a world flooded with news sources, some reliable and others not, news literacy equips individuals with the skills needed to differentiate between trustworthy journalism and biased or false reporting. This literacy enables people to be informed and engaged citizens.
Media Literacy
Media literacy involves the ability to access, analyze, evaluate, create, and act using all forms of communication, including print, television, radio, and digital media. It empowers individuals to decode messages conveyed through various media channels and discern between genuine content and manipulated or biased narratives.
Disciplinary Literacy
Disciplinary literacy pertains to the ability to work within specific academic disciplines, such as mathematics, science, and literature. It involves understanding the unique language, terminology, and methodologies of each field, enabling individuals to engage more deeply with subject matter.
Information Literacy
Information literacy encompasses the skills required for recognizing when information is needed, locating reliable sources, evaluating the credibility of information, and effectively using it to meet specific needs. This literacy is essential for decision-making, problem-solving, and lifelong learning.
Types of Misinformation and Disinformation
Understanding the different types of misinformation and disinformation is essential for recognizing and combatting false or misleading content:
Satire or Parody
Satire or parody content is created without the intent to cause harm, but it has the potential to deceive. Such content is often humorous or ironic and may be mistaken for genuine information, leading to misunderstandings.
Misleading Content
Misleading content involves using accurate information to frame an issue or individual in a misleading or biased way. It aims to manipulate the audience’s perception by presenting facts out of context or with a particular slant.
Impostor Content
Impostor content occurs when genuine sources or people are impersonated to spread false information. This form of disinformation can harm reputations and credibility.
Fabricated Content
Fabricated content is entirely false and designed to deceive and harm. It may include fake news stories, manipulated images, or fabricated quotes, all aimed at misleading the audience.
False Connection
False connection occurs when headlines, visuals, or captions do not support the content they accompany. This misalignment between the text and visuals can lead to misconceptions.
False Context
False context involves sharing genuine content with misleading or false contextual information. This deceptive practice can change the interpretation of a piece of information, leading to misunderstandings.
Manipulated Content
Manipulated content entails altering genuine information or imagery to deceive the audience. Techniques may include photo manipulation, video editing, or audio tampering, all of which distort the truth.
In today’s digital age, the ability to distinguish between misinformation and disinformation and the various forms of literacy are paramount. Digital literacy, news literacy, media literacy, disciplinary literacy, and information literacy collectively equip individuals with the skills needed to critically evaluate information and navigate the complex information landscape. Moreover, recognizing the different types of misinformation and disinformation empowers individuals to be discerning consumers of information and contributes to a more informed and resilient society.
The Meridian International Center, supported by the U.S. State Department through the U.S. Embassy in Colombo, organized the South & Central Asian SCA Reporting Tour. Its goal was to empower journalists from Nepal, Bangladesh, India, and Sri Lanka with knowledge about disinformation, ethics, and credibility. They received training from various institutions like Poynter, Axios, Voice of America, RAND, IREX, and Duke’s Reporters’ Lab, covering topics like disinformation, fake news, recognizing campaigns, and how to counter them. This article explores the impact of the tour.

